The Cutaneous Screening and Melanoma Diagnosis Unit at the Institut de Dermatologia Garcés, led by Dr. Joan Dalmau, has different specialized diagnostic techniques available to assess any pathology in the skin, hair and nails. This ensures that each patient receives the most precise diagnosis possible.
Diagnosis of Skin Cancer and Melanoma
Because of the importance of early diagnosis, the Diagnosis Unit has specialized above all in the diagnosis and control of pigmented lesions on our patients to ensure the early detection of skin cancer in general and of melanoma in particular.
Our diagnostic techniques
Cutaneous screening is the diagnostic test of choice to monitor nevi, freckles or moles.
The screening process begins with obtaining the patient’s medical history and performing a clinical exploration in order to determine the risk factors and the patient’s skin type.
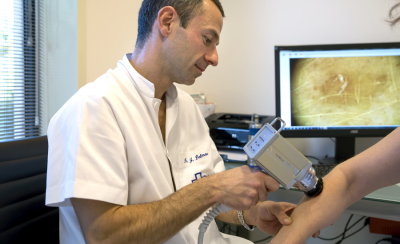
The dermatologist then takes a total body digital image, a visual map of the entire body, to monitor the evolution of the nevi. The technique employed for this is digital epiluminescence dermatoscopy.
High-resolution reproductions of all the nevi localized on the body map are printed and then analyzed in a report which is given to the patient.
Although this technique is generally used for the early detection of skin cancer in general and melanoma in particular, it is also used for the diagnosis of any cutaneous lesion as it captures high-precision images of any alteration which may appear on the skin, hair and nails.
A sentinel node biopsy is a test related to the diagnosis of melanoma which detects whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body, thereby determining the extension and location of the tumor.
The test is performed by injecting a radioactive substance into the lymph vessels near the tumor. Using a camera, the doctors can see if the substance accumulates in any of the sentinel nodes, the nodes which warn of the presence of the tumor. If any of the nodes are affected, they are removed for subsequent analysis.
A biopsy is a diagnostic test which takes a skin sample so it can be analyzed under a microscope. This technique is generally used in the case of skin cancer or melanoma as it allows doctors to determine whether a lesion contains malignant cells.
To take the sample, a local anesthetic is applied and in some cases the biopsy may leave a small scar.
A PET scan is a diagnostic method to determine the presence of cells of malignant tumors in the body and it is used to determine whether the skin cancer or melanoma has spread in the body, in other words to see whether it has metastasized.
The technique functions with an injection of a substance called radioactive glucose. All cells use glucose but tumorous cells are more active and consume more glucose than the other cells in the body.
Once the substance has been injected, a scan is taken which reacts to the cells with glucose. Due to the presence of a larger quantity of glucose, the tumorous cells appear as brighter spots in the image and therefore their location can be detected.
